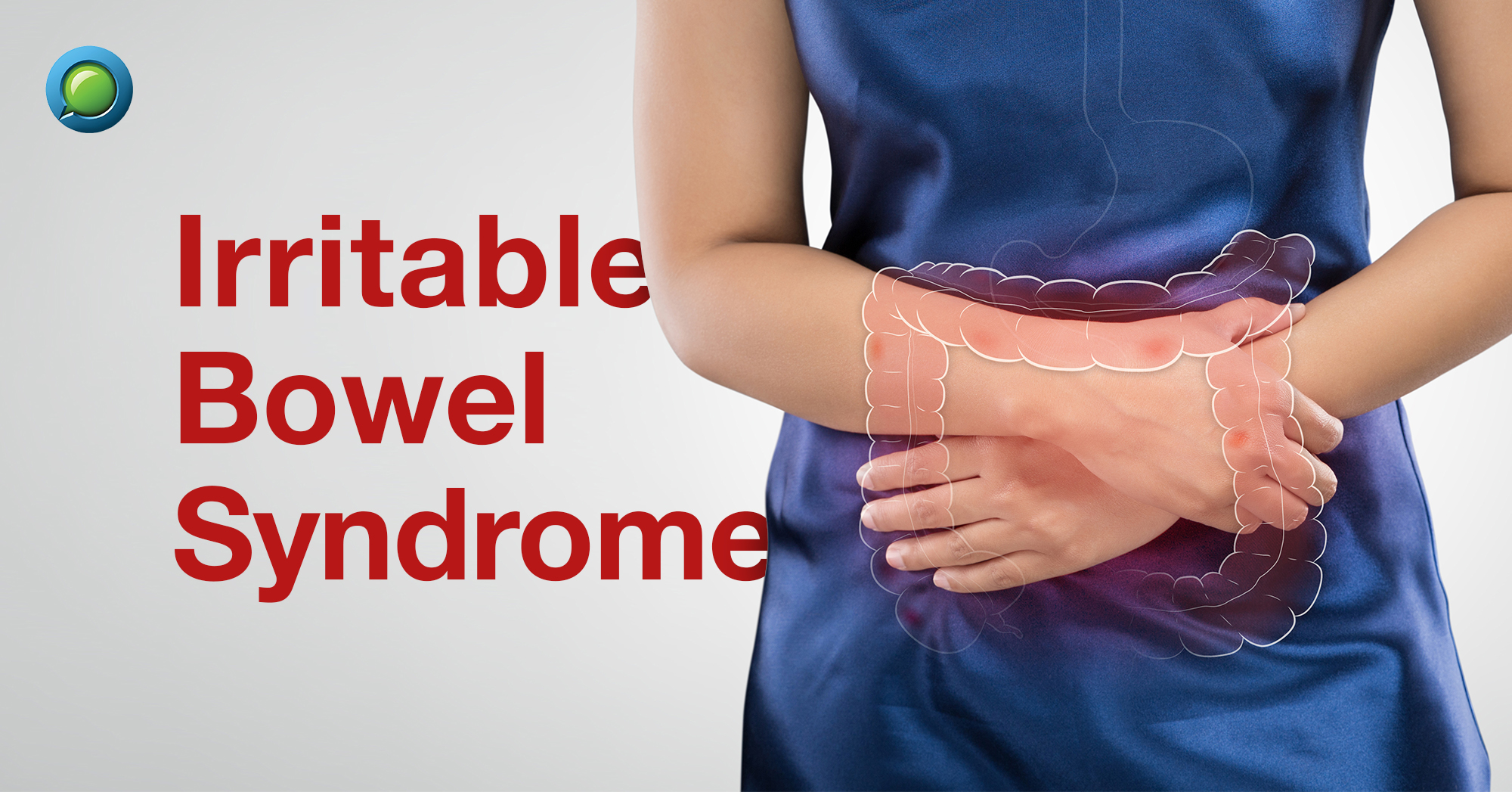
IBS is a chronic gastrointestinal disorder characterized by alterations of bowel habits [changes in frequency or form of bowel movements] and abdominal pain with signs of no damage due to disease.
How common is IBS?
IBS is a common disorder accounting for 11.2% of the global prevalence and reported 4.2% -7.5% prevalence in the Indian population. The condition however remains underdiagnosed as patients neglect the symptoms and rely on self-care.
Is IBS a “serious illness”?
The severity varies from person to person with some people experience mild symptoms that come and go while others may have severe daily bowel issues that impact the quality of life and poses a significant burden on daily activities. Sometimes, there are periods of acute exacerbation of symptoms in otherwise mild IBS patients.
What are the symptoms of IBS?
IBS [also known as mucus colitis, nervous colon, spastic colon, Irritable colon] affects the large bowel causing discomfort and digestive issues
Symptoms may include
- Pain [usaually lower part of abdomen] /cramps that worsen after meals and improve after a bowel movement
- Diarrhea, Constipation, or alternating pattern between two
- Harder or looser stools than usual
- Excess Gas or bloating of the abdomen
- Sudden urge to go to the bathroom
- Straining while defaecation/Sense of incomplete evacuation
- Mucus in poop
- Food intolerance [Lactose, Gluten]
- Fatigue and Sleep disturbances
- Anxiety/Depression
Who is at risk for developing IBS?
A young [age <50] female with a family history of IBS is at higher risk. Emotional stress, anxiety, GI infections, food intolerances may trigger or worsen the symptoms of IBS.
Causes of IBS – Unsolved Puzzle…
The exact cause is not known but a combination of certain factors may contribute to the development of IBS such as
- Alterations in intestinal motility, permeability, nutrient absorption & gut microbes
- Hypersensitive nerves in the bowel wall
- Poor coordination between the brain and gut
How do u know if u have IBS?
There is no specific test to diagnose IBS. Complete Medical history, physical exam, and tests [Blood tests, stool samples, X-rays, and Colonoscopy] are done to rule out other conditions.
IBS is diagnosed by using Rome criteria
- Recurrent abdominal pain [weekly pain for the last 3 months ] combined with at least 1 of the following
- Pain relieved by bowel movements
- Changes in frequency or form of bowel movements
Types of IBS
There are 3 types of IBS depending on the predominant bowel habit [Table 1]
Table 1: Types of IBS| Types | Predominant Symptom |
|---|---|
| IBS-D | Diarrhea |
| IBS-C | Constipation |
| IBS-M (mixed type) | Alternating constipation, diarrhea, or neither |
What is the treatment for IBS?
Treatment includes diet and lifestyle modification along with therapies to relieve symptoms such as fiber-consumption/laxatives for constipation, antidiarrheals, smooth muscle relaxants for pain, and psychotropic agents for pain, diarrhea, and depression.
Table 2: Dos and Don’ts for IBS| Dos | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Eat fiber-rich fruits, vegetables, grains, and nuts | Don't skip meals |
| Drink plenty of water | Avoid foods that trigger your symptoms |
| Exercise regularly | Avoid fatty, spicy, processed foods |
| Get enough sleep | Limit caffeine (coffee, chocolate, teas, sodas) |
| Practice yoga/meditation to keep stress away | Don’t smoke |
| Add probiotics to the diet | Avoid alcohol and sugary beverages |
A low FODMAP diet has shown satisfactory symptomatic improvements in IBS. Talk to a dietitian at DocOnline for guidance on diet changes.
Few psychological interventions including Hypnotherapy, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Biofeedback have shown good results in patients with moderate to severe IBS who do not respond well to medical therapy.